

|
Introductiongds2oasfrac is a library that reads a GDSII file, fractures it into trapezoids and creates output in the new OASIS format. It is intended to be incorporated into an application used for preparing IC layout data for a mask writer. Currently it is available for Windows (32 bit) but can be easily made available on 64 bit Linux and Solaris as needed. 
BackgroundChip layout data in GDSII format must be "fractured" in order that a mask writer can use the data. The fractured data was normally produced in a specialized and proprietary format for each mask writer - for example, the ETEC mask writers required a format known as MEBES. Over the years there were mutltiple versions of MEBES released in order to support more capable machines and larger databases. While ETEC dominated the mask writer market for some years, other manufacturers of mask writers defined their own data formats. This required fracturing software to support a large number of different output formats. Later a new generation of mask writers were developed in Japan that used a variable shape beam and these new machines also had their own data formats. When the OASIS specification was developed as a replacement for GDSII, a portion of the specification was also created optimized for use by mask writers. Until recently, no mask company directly read the OASIS format due to legacy reasons. However a new machine, recently developed, uses the OASIS format for its input and Artwork has developed an efficient yet low cost fracturing engine for it. Why Fracture to Trapezoids?Vector data input to a mask writer must be optimized for very fast rasterization. 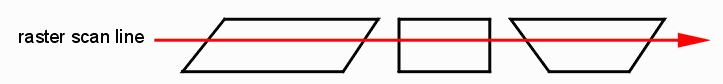
Figures that are convex in one direction (we call this convex in X) can be very efficiently rasterized with minimum computation. For 90 degree data the trapezoid reduces to a rectangle. FunctionalityLayer Control The user can specify which layers to fracture. Each GDSII layer is mapped to the equivalent layer in OASIS. Currently there is no data type discrimination. Output Grid Snap The user can specify an output grid and fractured data will be snapped to the specified grid. OASIS native grid is 0.001 um (1 nm) but the user can specify a coarser grid such as 0.01 um if needed. Overlap Removal Input data is unionized so that the output fractured data has no overlap. 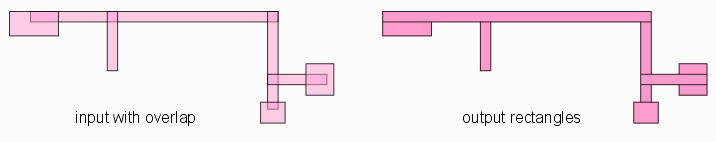
Polygon Sorting Polygon data within a tile can be sorted by X and Y. The min X and min Y coordinate of the polygon are used for the sort. Tiling The user can specify a square or rectangular tile size or alternately, the number of tiles desired and the program will then computed the required tile size. The contents of each "tile" are saved in a cell or structure which is labeled by its position in the array. 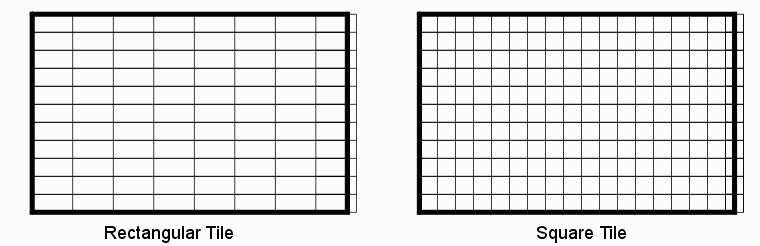
Tile Order Sorting An option can be turned on to sort the tiles within the OASIS file from top to bottom. The illustration below shows how the tiles are labeled and how the OASIS file is organized.
Transformations The following transformations can be applied to tiled output data.
Enlarge or reduce the size of the whole figure in a uniform ratio. This is generally a small value such as 1.0002 to account for process shrinkage or expansion. MirroringReflect the output data about X-axis or Y-axis RotationRotate the output data about the origin point. Only 0 90 180 and 270 rotations make sense. OASIS.VSB Compliant The resulting OASIS file is OASIS.VSB compliant. This means that it includes the required records and follows restrictions required for input to electron beam conversion tools as defined in 2005 by Selete. For example, all output figures are written as either rectangles, trapezoids or ctrapezoids. All cell placements have insertion scale=1,rotation=0 and mirror=0. 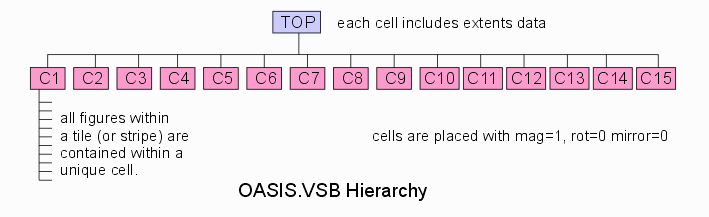 Multi-threaded The program is multi-threaded and can make use of multiple CPU cores. Second GenerationBased on results from the prototype imaging machines, new features are implemented for the second generation rasterizer. Click here to read the second generation specifications ... |