

|
Execution Control FunctionsThese functions are used to control how the library will work in terms of processing polygons and creating the output. Any user of the library should understand the default behavior of the various settings and the available options and set them as needed prior to calling the actual boolean operation. |
QisBoolOptions_ResetSyntax: QisBoolOptions_Reset ( void *bdll_handle); Function: resets all options back to their defaults. Inputs: bdll_handle:- thread handle QisBoolOptions_SetMaxPoints
Syntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetMaxPoints(int maxpts, void *bdll_handle); Function: Used to define the maximum number of vertex points in any returned polygon. Any output polygon that has more than the max number of vertices will be "fractured" by slicing it. Inputs: maxpts: the maximum number of points for any non-Leonov polygon. Notes If not set, boolean will not fracture any output polygon. Leonov output is not restricted with respect to vertex count. Example To set the maximum number of vertices per polygon to 4096 (for handle=1) void QisBoolOptions_SetMaxPoints(4096, 1); |
QisBoolOptions_SetClipWindow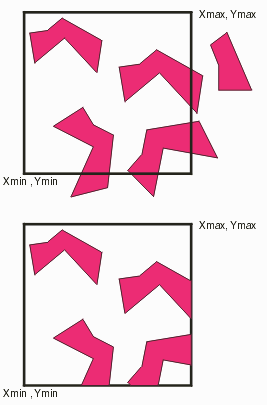
Syntax:
void QisBoolOptions_SetClipWindow
(int iMinX, int iMinY, int iMaxX, int iMaxY,
void* iBooleanHandle
);
Function: Defines a rectangular window that acts as a filter for all input polygons to QisBool functions; data completely outside the window is ignored. Data crossing the window is clipped to the window edge during boolean operations. Once this window is set, if you wish to remove the window filter for subsequent function calls, you must set Xmin,Ymin to -MAXINT and Xmax,Ymax to MAXINT. MAXINT = 2,147,483,000 OR use QisBoolOptions_Reset. Inputs: iMinX - lowest X value of Window iMinY - lowest Y value of Window iMaxX - highest X value of Window iMaxY - highest Y value of Window iBooleanHandle - handle for this thread QisBoolOptions_SetPartition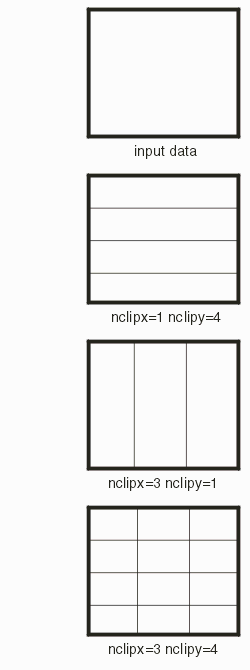
Syntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetPartition ( int nclipx, int nclipy, int mode, void *bdll_handle ); Function: Used when processing large data sets to control how the bool library subdivides the problem to keep in the "linear" data space range. Except for special cases the automatic mode should be used. Used in conjunction with QisBoolOptions_SetPartitioningThreshold which determines, in automatic mode, the number of vertices per partition. In automatic mode, the stripes run horizontally. Inputs: nclipx - number of subdivisions along X nclipy - number of subdivisions along y partitioning mode
Manifest constants are: BOOL_PART_MODE_NONE 0 BOOL_PART_MODE_AUTO 1 BOOL_PART_MODE_MANUAL 2 If partition mode is set to manual the parameters nclipx and nclipy are used. Otherwise they are ignored. bdll_handle - handle for this thread Default BOOL_PART_MODE_NONE - no partitioningQisBoolOptions_SetSizing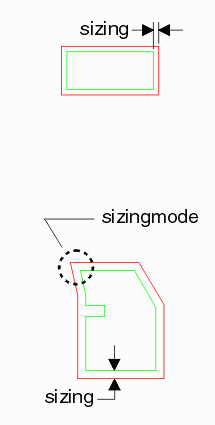
Syntax:
void QisBoolOptions_SetSizing
(double iValue,
void* iBooleanHandle
);
Function: Used to define the amount of edge sizing. Inputs: double iValue- value for the parameter iBooleanHandle- handle for this instance Even though the parameter is defined as a double, this is just a convenience for the programmer; the values used by the library will be rounded to the nearest integer - i.e. a sliver of 1.56 will be converted to 2. Example You wish to size up all polygons by 0.5 um. The user units are in um and the resolution is set such that: 1 um = 1000 db integers. Therefore the sizing = 500. The handle for this thread is assumed = 1 void QisBoolOptions_SetSizing (500,1); Related Functions see functions: QisBoolOptions_SetSizingMode and QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners BoolSetLogFileParm_MTSyntax: void BoolSetLogFileParm_MT ( int type, const char * value, void *bdll_handle ); Function: Used to re-define the name and location of the log file output from the default. Inputs: int type
REMLOGFILENAME_PARM - removes the log file when the instance is closed. const char * value: string of path/name bdll_handle: thread handle Default Behavior the default log file name is Results_N.txt where N is the handle of this instance. The default behavior is to not delete the log file when the instance is closed. QisBoolOptions_SetNonIsotrSizingSyntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetNonIsotrSizing ( double szx, double szy, void *bdll_handle ); Function: Used to define sizing value when non isotropic sizing is requested. This allows independent sizing in X and Y. Inputs: szx - sizing in X direction (even though this is a double, the actual sizing value is rounded to the nearest integer.) szy - sizing in Y direction (even though this is a double, the actual sizing value is rounded to the nearest integer.) bdll_handle: thread handle Related Functions QisBoolOptions_SetSizingModeQisBoolOptions_SetSizingModeSyntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetSizingMode ( int mode, void *bdll_handle ); Function: Used to turn on and set polygon sizing behaviour. See the sizing page for details. Inputs: mode NO_SIZING 0 - no sizing STD_SIZING 1 - standard mode; ISOTR_SIZING 2 - see flavors NONISOTR_SIZING 3 - see flavors bdll_handle - thread handle Related Functions QisBoolOptions_SetSizing is used to set the actual sizing value and also the smoothing parameter and sliver removal parameter. QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners sets the handling of corners for ISOTR_SIZING and NONISOTR_SIZING. QisBoolOptions_SetNonIsotrSizing sets the sizing values when non-isotropic sizing is requested. 
QisBoolOptions_SetReturnSliceEdgesSyntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetReturnSliceEdges(int flag, void *bdll_handle); Function: Activates a mode such that when polygons are modified (sliced) to accomodate the maximum vertex count restriction AND the output type for polygons has been set to "butting" then the slice edges will be returned in a call to QisBool_GetSliceEdges. A memory leak will occur if this mode is set and QisBool_GetSliceEdges is not called and followed with a call to QisBool_Release.Inputs: int flag - 0 off, 1 on bdll_handle: thread handle Related Functions QisBool_GetSliceEdges QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners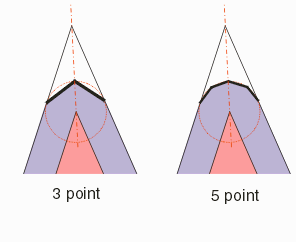
Syntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetRoundCorners( int mode, void *bdll_handle ); Function: Controls the sizing behavior at corners of the polgyon when the sizing mode = Incremental. Typically this is only necessary when polygons exhibit "sharp" corners. If the input data is known to be Manhattan then one would normally select the RIGHT_ANGLE_CORNER mode. See the sizing page for details. Inputs: mode
RIGHT_ANGLE_CORNER
THREE_POINT_CORNER
FIVE_POINT_CORNER
bdll_handle: thread handle Related Functions QisBoolOptions_SetSizingMode QisBoolOptions_SetPartitioningThreshold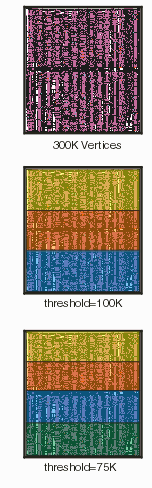
Syntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetPartitioningThreshold( int N, void *bdll_handle ); Function: If data partioning is set to automatic, then this parameter determines the number of vertices per partition. If not explicitly set by the calling program, the default value = 100,000. This parameter need only be set when Bool_Partitition_Mode = AUTO Inputs: int N - value, which if exceeded will trigger partioning bdll_handle: thread handle Related Functions 
QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovInput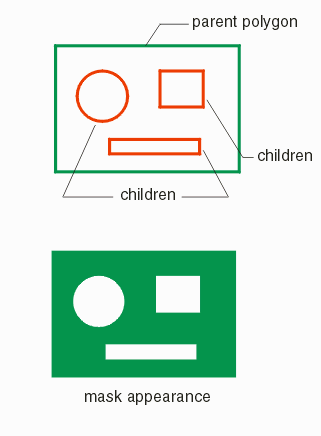
Syntax:
void Function: tells the boolean whether the input polygon arrays (A and B) are in standard or in Leonov format. A Leonov polygon consists of a single parent polygon followed by one or more children. The children are completely contained within the parent and represent cutout's of the parents interior. Inputs: operand_flag LEONOV_OPERAND_A LEONOV_OPERAND_B LEONOV_OPERAND_BOTH bdll_handle: thread handle mode ON OFF Notes For Leonov polygons, to differentiate the parent polygon from its children, the vertex count of the parent is a negative integer and the vertex count for each child polygon is a positive integer. Related Function QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovOutputSyntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetLeonovOutput( short mode, void *bdll_handle ); Function: instructs the library how to output polygons. This affects polygons with "islands" or "holes." There are three options: Leonov, in which there is a single parent polygon followed by one or more children (representig the holes), butting, where a polygon with holes is sliced until there are no more holes, or cut lines (STD), where a polygon with holes is represented by using one or more cut lines that flow into and out of the polygon. Inputs: mode OUTPUT_MODE_STDOUTPUT_MODE_LEONOV OUTPUT_MODE_BUTTING bdll_handle: thread handle Notes In order to differentiate the parent from its children in Leonov polygons, the vertex count of the parent is a negative integer and the vertex count for each child polygon is a positive integer. QisBoolOptions_SetConvexOutput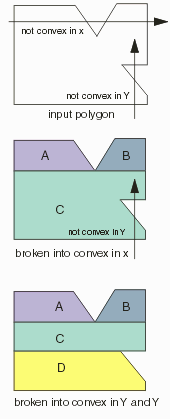
Syntax:
void QisBoolOptions_SetConvexOutput
( EConvexOutput iMode,
void* iBooleanHandle
);
Function: this parameter determines whether the output polygons should be tested for, and made convex. There are three options: no testing, convex-in-x only and convex in x-and-y. Note that if the input data is Manhattan, then the results will be rectangles; if the input data is all angle the results will be trapezoids. Inputs:
iMode
one of: eNO_CONVEX eCONVEX_IN_X eFULLY_CONVEX
void* iBooleanHandle
thread handle
Notes this option does not work when Leonov polygons have been selected for input/output. QisBoolOptions_SetTestManhattan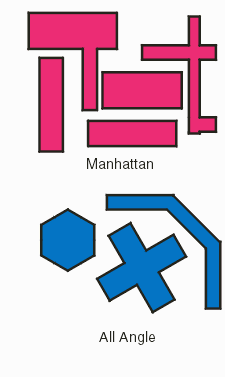
Syntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetTestManhattan(short ismanh, void *bdll_handle); Function: this parameter tells the boolean library that the input data should be tested to determine whether or not they are Manhattan.(i.e all 90 degree data) Certain algorithmic efficiencies are possible when the library knows it is processing Manhattan data. Inputs: ismanh: NOTEST4MANHATTAN TEST4MANHATTAN bdll_handle: thread handle Notes This function impacts the return code for QisBool_Booleanize. If TEST4MANHATTAN is set, the QisBool_Booleanize returns 2 if in fact the input set is all Manhattan and no illegally crossing polygons are found; The QisBool_Booleanize returns 0 if the input polygon list contains non-Manhattan polygons but no illegal polygons; it returns the number of illegal polygons as a negative number. QisBoolOptions_SetEdgePtCompensationSyntax: void QisBoolOptions_SetEdgePtCompensation(int width, void *bdll_handle); Function: Compensates the coordinates returned by QisBool_GetSliceEdges to account for the "width" of a so called patch line that a calling program will use later to cover up any butting edges. The user defines a "width" and the end points of the edges are "pulled back" based on the line width. See illustration. 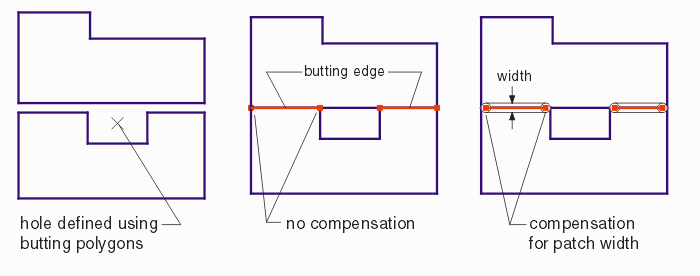
Inputs: width - the width of the round draw used to "patch" the cut line or slice line bdll_handle - the thread's handle Related Functions QisBool_GetSliceEdges |