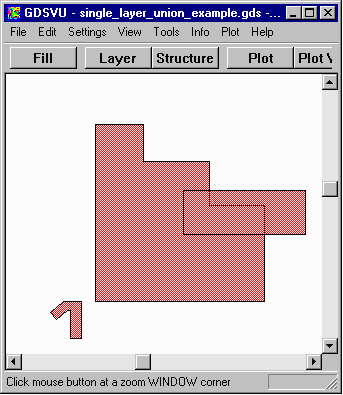
This example illustrates how you would combine all of the overlapping and touching polygons on a single GDSII layer. The operation is unary because we have only one "input" to deal with.
Operation: Unary UnionLayer=1
|
single_layer_union_example.gds This example illustrates how you would combine all of the overlapping and touching polygons on a single GDSII layer. The operation is unary because we have only one "input" to deal with. Operation: Unary UnionLayer=1 |

|
|
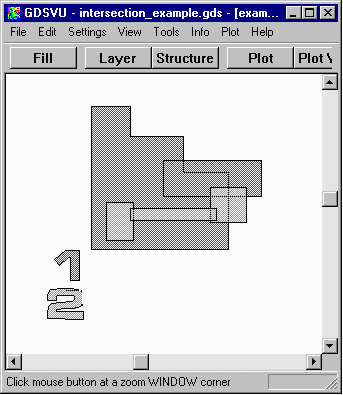
intersection_example.gds This example shows how to find the intersection between two separate inputs. In this particular example the two inputs come from the same GDSII file but they could have come from separate GDSII files also. Operation: Binary And Primary Operand Layer=1 Secondary Operand Layer=2 |
|
|
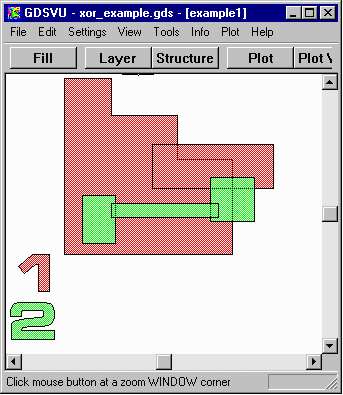
xor_example.gds The XOR operation is a very common one for comparing two layouts to see the just the differences. If the two layouts are identical the output will be empty. QckBool also has a special function that can be used after XOR to find the differences as they may be extremely small. Operation: Binary XOR Primary Operand Layer=1 Secondary Operand Layer=2 |
|
|
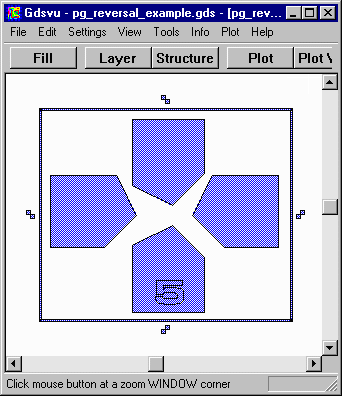
pg_reversal_example.gds You can try this two different ways. First use the extents calculated by the program. (96,441,789,1035). Then add a margin of 100 um to the data window. (46,391,839,1085). Operation: Unary Image Reversal Primary Operand Layer=5 Window=(96,441,789,1035) Primary Operand Layer=5 Window=(46,391,839,1085) |
|
 Image reversal to data extents
Image reversal to data extents |
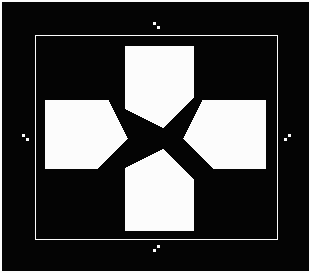 Reversal using a window that gives 100 um margin.
Reversal using a window that gives 100 um margin. |
| QckBool Page | User Interface | Download | Revision History | Price |