Sample Polygon Data Structure
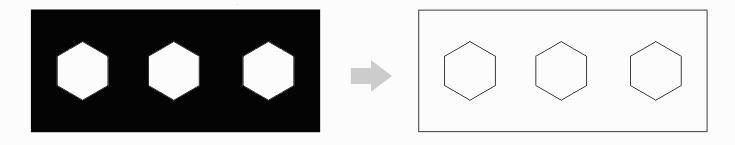
Consider the filled region shown below at left. It can be represented as a Leonov polygon: a rectangular parent polygon containing three child polygons. This is a common occurrence in Gerber files with negative ground planes.
The data returned by GBRUnion DLL is organized as follows:
typedef struct
{
int Layer; -- if Leonov needs layer for embedding level output
int Vsize; -- 5 if circular; 2 if no arcs in polygon
int VCnt; -- Vertex count of single or container polygon
double *XY; -- list of XY coordinates for the container (parent) polygon
int HoleCnt; -- Number of holes in container polygon
int *HoleVCnts; -- list of vertex counts for each contained hole
double **HoleXYs; -- list of XY data for each contained hole
} ACS_GBRUNION_Polygon;
Layer - for Leonov polygons a layer is needed to hold the embedded polygons.
Vsize - either 2 or 5 depending on whether the polygon has only straight edges (2) or circular data (5).
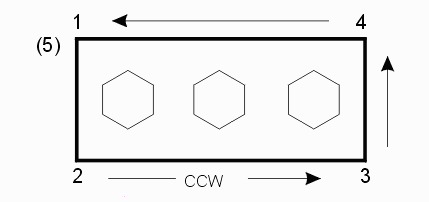
Vcnt - the number of vertices in the parent. Note that since we adhere to the GDSII description of polygons for our internal database the first vertex is counted twice - once at the beginnning and once at the end. In this example Vcnt=5
double *XY - coordinates of the parent polygon.
holecount - the number of child polygons. Note that child polygons may not touch the parent nor touch each other. In this example holecnt = 3
*HoleVCnts - a list of the vertex counts for the child polygons. In this example we have three children and each has 7 vertcies. In this example the list would look like: 7 7 7
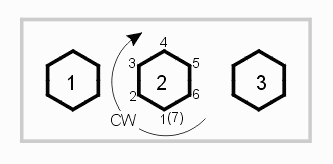
**HoleXYs - list of the XY coordinates for the children polygons.
If a polygon is of type re-entrant or butting, then it won't have any internal holes and only Vsize, VCnt and *XY are of interest.
